Human papillomavirus (HPV) is spread through contact and/or sexual contact. HPV has been known for more than 70 years. In 1935, it was shown that this group of viruses can cause the development of papillomas and skin cancer in rabbits. Since then, there has been no doubt that HPV can cause cancer in mammals (including humans), but for some reason only now have they started to scare us about this disease and its consequences. While in the human body, different types of HPV manifest in different ways. But the unifying feature of these viruses is their ability to cause various forms of papillomas (warts).
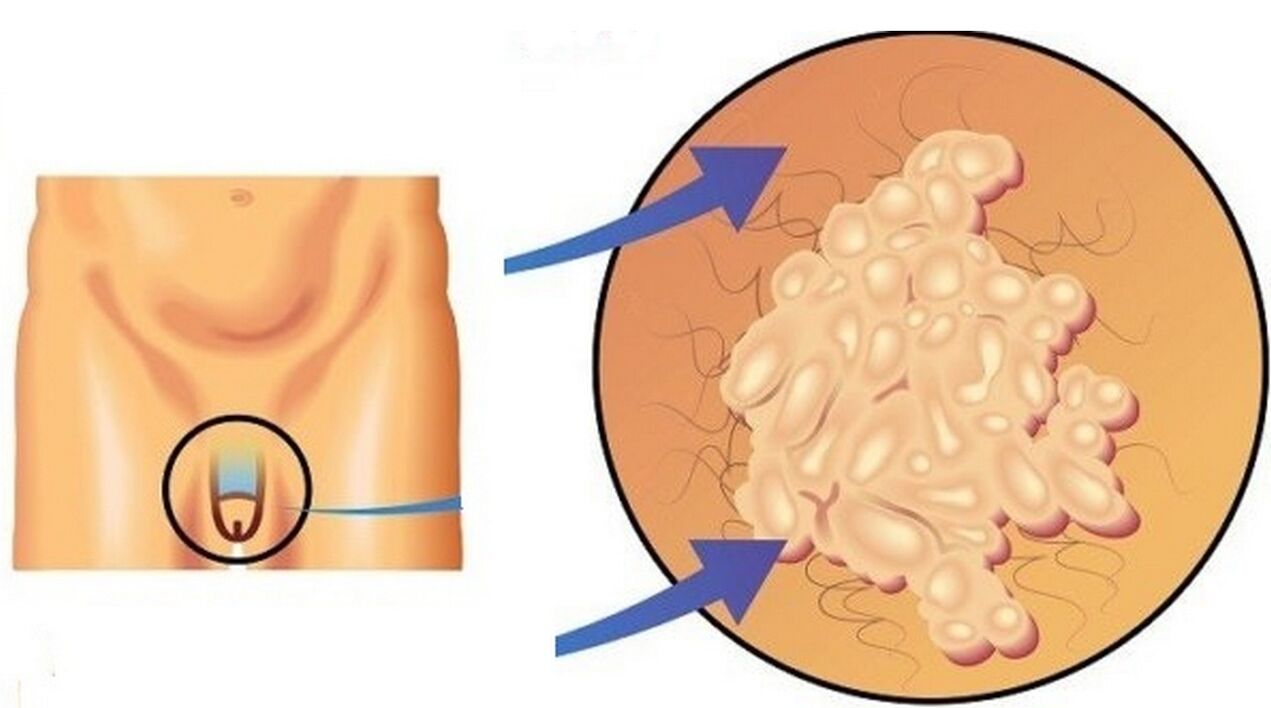
Approximately 1-3% of people infected with HPV develop papillomas at the site of primary contact. Papilloma is considered by doctors to be a benign tumor and does not pose a significant threat. Although any change in normal cell growth in the form of a tumor or spot alerts both the patient and the doctor. In some cases, HPV manifests itself exclusively as a dermatological disease with contact-household transmission. HPV can also occur as a sexually transmitted disease, causing genital forms of sexually transmitted papillomas. Because cancer is extremely rare in the cutaneous forms of HPV, we will focus more on the genital forms of HPV, which are much more likely to cause cancer. Genital forms of HPV are caused by about 40 of the 130 known types of the virus. According to estimates, up to 70% of the sexually active adult population will be infected with genital forms of HPV during their lifetime.
Of course, sexual activity does not mean "obsolete" monogamous relationships. In fact, provided that both partners have never had another sexual relationship, the probability of genital forms of HPV is almost zero. With each new partner, the risk of infection increases significantly. Moreover, with multiple HPVs at the same timecan be infected, not to mention other sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). Unlike most other infections, where the main transmission factor is bodily fluids, HPV can be transmitted through skin-to-mucous contact. And if, for typical STDs, condoms areuse is a relatively reliable remedy, then in relation to HPV, as in the case of genital herpes, its effectiveness is rather doubtful.
Papillomas in men
In men, papilloma is a clinical manifestation of the patient's infection with the human papillomavirus. It must be said that the virus is quite common, but it is able to stay in the human body for a long time, it practically does not manifest itself externally. As a result of predisposing factors, the human papillomavirus is activated, resulting in the formation of various neoplasms of the skin and mucous membranes. Some virus types are characterized by oncogenic activity, so neoplasms that develop on the skin and mucous membranes must be treated with extreme caution and under the supervision of a doctor.
Papillomas in men: causes of occurrence
The cause of the appearance of papillomas on the body of men and women is a virus that can enter the body in different ways:
- Due to unprotected sexual contact: the most common type of infection, including the fact that a person can be a carrier of the virus for a long time without knowing it, since the virus can only manifest itself under the influence of external factors. . Infection is also possible through direct contact with mucous membranes. In this case, the risk of infection increases if the skin or mucous membrane is damaged (there are cracks, scratches, cuts, etc. ). Due to the prevalence of this cause of infection, it is understandable that papillomas (condylomas) appear very often in men and women in the intimate area, at points of contact, from which the risk of infection is generally higher in men. sexual activity is greater, but the mucous membrane of women is less protected.
- Through household contact: it has now been proven that the HPV virus can enter the human body through casual contact (even shaking hands), especially in public places (spa, swimming pool, gym, etc. ).
It should also be remembered that infection with the specified virus does not mean its manifestation.Most often, the disease becomes active and becomes noticeable when:
- the patient's immunity weakens;
- there was great physical or mental stress, stress, exhaustion;
- There are various sexually transmitted diseases.
Characteristics of the course of human papillomavirus infection in men
Under natural conditions, most viruses are of low pathogenicity due to low infectivity and host resistance to infection. When entering a human cell, the DNA virus most often does not integrate into the cell genome. Instead, a protein (or group of proteins) encoded by the viral genome rapidly activates the cell's DNA replication system. If the virus replicates synchronously with the cell without damaging it, a non-productive type of infection develops, otherwise this process is called persistence or asymptomatic carriage.
When the virus multiplies rapidly in a cell, the process is called asymptomatic carriage, or it releases thousands of active virus particles. This period is characterized by the appearance of rounded formations and growths on the skin and mucous membrane. However, HPV types 16 and 18 can integrate into the cell genome without hijacking the cell's genes. This phenomenon is called "insertion mutagenesis", and the gene that has been changed in this way is inherited by all the descendants of that cell. As a result, oncogenes are activated and a tumor appears. Thus, these cells are inherited by all descendants from the formation of the fetus, the woman's pregnancy and the childduring his birth.
The main factors of infection
- multiple sexual partners;
- use of birth control pills;
- smoking;
- insufficiency of cellular immunity (anemia, thyroid pathology, presence of chronic coccal infections - tonsillitis, sinusitis, caries);
- artificial diet restriction, weight loss.
With good immune status, the virus is cleared from the woman's body in 50% of HPV infections within one year, and in 85% of cases within 4 years. This is why the number of women infected with HPV decreases with age. The development of cancer in men and women is closely related to human papillomavirus infection. Genital warts, body papillomas, warts and flat warts were discovered as a result of the study of men and women infected with human papillomavirus infection.
HPV in men: consequences
The virus can cause condylomas, or genital warts, which, as the name suggests, are found in the groin and on the head and foreskin of the penis. Condylomas of this type have very dangerous consequences for men and require treatment. Condylomas on the penis can lead to narrowing of the foreskin, which can make it difficult to expose the head of the penis and cause problems in your personal life. It should also be remembered that in some cases such formations are not indicators of HPV, but of other sexually transmitted diseases that have not yet appeared (for example, syphilis). Another danger of HPV is that the carrier of the virus can pass it on to his partner, thereby risking the development of cancer. The virus can also be transmitted from an infected mother to the fetus, so couples wishing to conceive a child should pay special attention to HPV and other such diseases.
HPV in men: symptoms
Most often, HPV can be present in the human body for a long time without showing itself. However, the most important sign (symptom) of the possible presence of HPV in men and women is the appearance of condylomas and papillomas - warts, nodules and skin irregularities - on the skin and mucous membranes, including the groin or vulva. , the color of which does not differ from the main skin.Condyloma- This is a genital type of papilloma that looks like a small growth that is connected to the mucous membrane with a kind of "leg". The size of the condylomas can vary from a few millimeters to a few centimeters - in the latter case, we are talking about an accumulation of condylomas. Such papillomas can appear on the head of the penis, thealso on the foreskin and around the anus (there is a high probability that there may be condylomas in the anus as well). Most often they are painless, but in some cases men may experience additional symptoms of human papillomavirus if the disease manifests itself as follows:
- pain when urinating, defecating or having sex;
- bleeding of condylomas: sometimes ulcers that do not heal for a long time may develop in their place;
- sometimes condylomas can also itch.
The listed symptoms usually indicate damage to the condyloma.
Treatment of HPV in men
Initial examination
In addition to the presence of HPV in the human body, the appearance of papillomas indicates the exhaustion of the immune system and the possible presence of other sexually transmitted diseases. In addition, certain types of papillomas, especially condylomas on the head of the penis, have a high oncological potential, so it is necessary to consult a specialist at the first signs of the disease. The sooner you start treating the human papillomavirus, the more chances a man has to avoid the serious health consequences of condylomas. (All of the above applies to women as well. )
Initial date
The initial appointment with the specialist involves a thorough visual inspection of the patient's mucous membrane and skin, as well as questioning and prescription of tests. Although papillomas most often have a characteristic appearance, additional tests and diagnostics make it possible to determine the presence of HPV in the patient's body with absolute precision. If HPV infection is suspected in men, the following tests are usually prescribed::
- blood test (for condylomas, urethral discharge analysis as well): modern diagnostic methods make it possible to isolate the DNA of the virus from the available material, thereby confirming its presence in the patient's body;
- biopsy of papillomas (condylomas): used to determine the presence or absence of cancer cells in the tumors.
Additional regimen
The treatment of human papillomavirus in men is largely determined by the presence or absence of genital warts. As with the herpes virus, it is almost impossible to completely get rid of HPV, so therapeutic effects and surgical interventions are usually aimed at eliminating the manifestations and increasing the duration of remission. Removal of HPV papillomas is not indicated in all cases. If the papilloma does not pose a danger and does not bother the patient, it cannot be removed at his request, but he must undergo regular preventive examinations. Removal is a mandatory treatment for genital warts in men, due to their special location.
Methods of disposal are different and are selected individually, including depending on the location of the tumors. In addition to the removal of tumors, the treatment of condylomas in men involves the use of drugs that help strengthen the immune system so that the body can fight the virus and suppress it, thereby suppressing its manifestations. Depending on the chosen method of getting rid of condylomas, the patient may also be prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs. By the way, no technique can completely rid a person of the infection: the disease is only "suppressed". The therapy is combined and includes the removal of skin growths and the use of drugs. The duration depends on the area affected.All skin tumors are removed in several ways:
- using cryodestruction (liquid nitrogen);
- diathermocoagulation (high-frequency current);
- electrocoagulation (cauterization with electric current);
- laser;
- chemical or surgical method etc.
In addition to local treatment, various antiviral drugs are also used. The main interferon preparations are:
- In addition to local treatment, various antiviral agents are used: human interferon;
- Viferon;
- cycloferon;
- reaferon;
- leukinferon etc.
Interferona substance produced by the human immune system to protect itself from viruses. Thanks to modern scientific progress in the field of genetic engineering, interferon-based drugs are produced by synthesis. This allows you to get a cleaner medicine (without impurities) and less allergenic. Interferon drugs are absorbed into the blood and have a systemic effect on the whole body. However, there are cases when interferon treatment causes allergic reactions. In this regard, these drugs are stopped and the doctor develops another drug regimen.
Dietary supplement(dietary supplement) for foods that contain indole-3-carbinol - the natural substance found in broccoli - the latest discovery of science. This chemical compound has a strong carcinogenic effect (it prevents the formation of malignant formations in the intestines, lungs, etc. ). It is noteworthy that indole-3-carbinol is found in most varieties of cabbage. It was established that the use of indinol increases the effectiveness of interferon treatment. However, this drug is still being tested and its effect on the body is being studied in detail. The doctor can prescribe non-specific immunomodulators.
It should not be forgotten that the functioning of the immune system is not completely known, as its state changes depending on each intervention: be it therapeutic or microbial. For this reason, immunomodulators should not be prescribed randomly. It should be remembered that antiviral drugs, such as antiviral drugs, which are particularly effective against the herpes simplex, herpes zoster (shingles) and chicken pox viruses, are ineffective in treating PVI. Therefore, their use is not practical.
During the treatment, the patient can also receive advice:
- refrain from sexual contact, especially without protection, to prevent the virus from entering the partner's body;
- Strengthen your immune system with diet and moderate physical activity.
The result of the treatment:It should be remembered that the process, timing and effectiveness of HPV treatment largely depends on the general condition of the patient's body, concurrent diseases, and the development of possible complications of the disease (primarily oncological).
Complications
The presence of papillomas and condylomas is a cosmetic defect. Growths in the genital area negatively affect a man's mental and sexual health and cause difficulties in communicating with the opposite sex. In addition, such a man is a source of infection for his sexual partners. With reduced immunity, condylomas can grow quickly, occupying a significant area. When the rectum is also involved in the process, a sensation of a foreign body appears in the rectum, rectal fissures and other proctological problems may develop. The spread of growths to the area of the urethra leads to the development of urological pathology. When formations are damaged, bleeding occurs. In case of infection, inflammation and suppuration begin, accompanied by pain, fever, weakness and general deterioration.
Prevention
The complexity of HPV treatment, as well as the serious health problems caused by the virus, determine the importance of preventive measures, which include:
- ordered to have sex with a trusted partner and use barrier-free contraception. At the same time, modern research shows that only high-quality protective equipment can significantly reduce the risk of HPV infection for both partners;
- strengthening the immune system: diet, taking vitamins, etc. ;
- the use of a special vaccine: in men, the process of drug treatment against human papillomavirus is three injections into the brachial muscle and can minimize the risk of the disease. The injection must be administered after prior consultation with a specialist (this prevention is only possible for persons not infected with HPV);
- preventive visits to the urologist to check for sexually transmitted diseases and other possible problems of the urogenital system, as well as to carry out tests to identify the virus.
If you notice characteristic formations in the intimate area, as well as in other parts of the body, on the skin and mucous membranes, you should consult a specialist as soon as possible. In this way, complications and other undesirable consequences for men's health can be avoided. In these cases, self-treatment is strongly not recommended, as only a specialist can diagnose and correctly prescribe the treatment of condyloma in men.
F. A. Q
What symptoms can papilloma cause in men?
In men, papillomas can appear as small warts or flat warts on the skin of the genitals, on or near the anus. Itching, discomfort or mild pain may also occur in the affected area.
How does papilloma spread in men?
In men, papillomas are spread through contact with infected skin or mucous membranes of the genitals. It can spread through sexual contact, as well as through direct contact with the affected area.
How to prevent papilloma infection in men?
In order to prevent papilloma infection in men, it is recommended to use a condom during sexual intercourse. Vaccination against human papillomavirus (HPV) can also reduce the risk of infection. Regular visits to the doctor and tests also help to identify the infection at an early stage and prevent its spread.
Useful tips
Tip #1
Consult a dermatovenerologist for professional advice and diagnosis. Only an experienced specialist can accurately determine whether the papilloma is dangerous and whether it is necessary to remove it.
Tip #2
Avoid damaging the papilloma. Do not try to remove it yourself, as this can lead to infection and complications. If the papilloma is in an area of friction or trauma (such as the neck or armpit), try using a soft bandage or tape to prevent damage.
Tip #3
Follow the hygiene rules. Wash and dry the area around the papilloma regularly to prevent bacterial growth and infection. Avoid sharing hygiene items (such as towels or razors) with others to avoid spreading the infection.















































































